As the global energy transition enters a more complex phase, all-solid-state batteries—renowned for their potential in safety, energy density and cycle life—are increasingly viewed as the crown jewel of next-generation storage technologies. Yet the path from laboratory prototypes to large-scale manufacturing remains fraught with technical hurdles. Among them, the stacking process has emerged as a key bottleneck that determines both cell performance and production consistency.
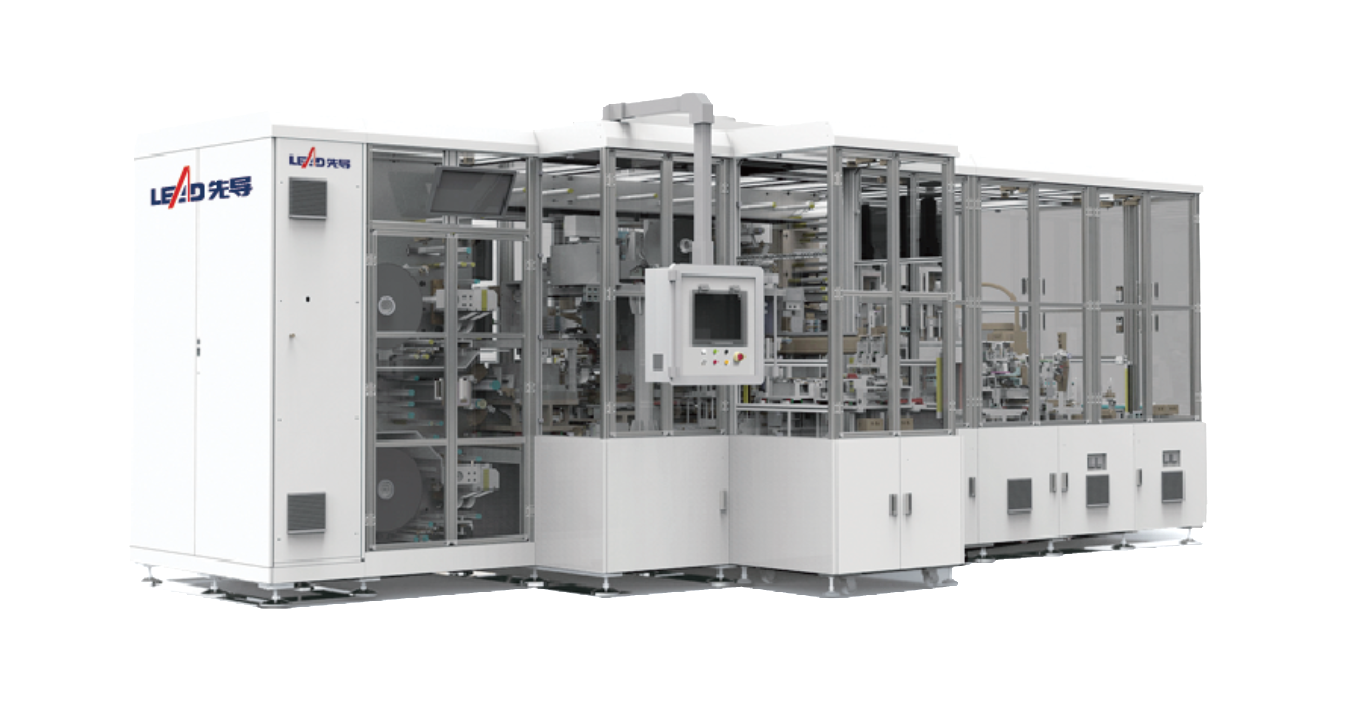
Against this backdrop, Lead Intelligent Equipment (hereafter referred to as LEAD) has leveraged its deep expertise in high-end equipment manufacturing to launch an integrated cutting-and-stacking system specifically designed for solid–solid interface requirements. The system aims to break through industrialization barriers and set a new benchmark for next-generation cell production.
Technical Challenges of Solid-State Batteries and the Critical Role of Stacking
The core of solid-state battery technology lies in replacing the liquid electrolyte and separator of conventional lithium-ion batteries with a solid electrolyte. The dominant technological pathways—oxides, sulfides and halides—each offer distinct performance attributes, but all face the same fundamental challenge: forming a stable, low-impedance solid–solid interface.
Unlike traditional “solid–liquid” contact, a solid electrolyte requires near-perfect interfacial intimacy with the electrode to ensure smooth lithium-ion transport. Oxide electrolytes are typically rigid ceramic sheets, while sulfide and halide systems provide better flexibility yet still struggle with sufficient interface contact. Under these constraints, stacking has become the most compatible and reliable solution for constructing high-performance solid-state cells. Its strengths lie in precise layer alignment, the ability to apply uniform pre-pressure and its compatibility with mechanically fragile materials.
As a result, stacking accuracy directly determines the effective contact area of the solid-solid interface and the uniformity of ion transport. These factors shape the cell’s internal resistance, rate performance and cycle life. Stacking efficiency, in turn, directly affects production cost and the feasibility of mass manufacturing—making it a critical differentiator for equipment suppliers.
Core Challenges in Solid-State Battery Stacking
The stacking process for solid-state batteries presents unprecedented demands compared with conventional lithium-ion equipment. These challenges stem largely from the unique chemical characteristics of solid electrolytes and the extreme requirements of the production environment:
Stringent Atmospheric Control
Sulfide and halide electrolytes are highly sensitive to moisture and oxygen, and can react to form toxic gases such as hydrogen sulfide while also degrading material performance. Stacking equipment must therefore deliver exceptional sealing and environmental control, operating reliably under ultra-low dew points and inert-gas protection.
Damage-Free Handling of Fragile Materials
Whether in the form of thin oxide ceramic sheets or compressed composite sulfide electrolytes, solid-state materials are brittle, fragile and prone to particle shedding. High-speed picking, transfer and stacking must be executed without causing material damage or contamination.
Extreme Requirements for Interface Pressure and Alignment Precision
To mitigate the risk of internal short circuits during densification processes such as hot pressing or isostatic pressing, the stacking step must achieve extremely high layer-to-layer alignment accuracy. It must also apply uniform, controlled pre-pressure to eliminate interfacial voids and enable the formation of a high-quality solid-solid interface. Conventional stacking platforms and pressure-control systems fall short of meeting these demands.
LEAD’s Comprehensive Optimization Framework
To address the challenges outlined above, LEAD has developed a new generation of integrated cutting-and-stacking equipment for solid-state batteries. The system delivers breakthroughs across three core technology dimensions, offering strong momentum for the industrialization of solid-state batteries.
Precision as an Advantage: Ultra-High-Accuracy Interface Engineering
- Breakthrough Alignment Precision
Leveraging high-frame-rate visual positioning with dynamic platform calibration, the system achieves an industry-leading ±0.15 mm interlayer alignment accuracy while effectively preventing particle shedding from porous and brittle materials.
- Dynamic Indentation-Elimination Technology
A dual closed-loop pressure–displacement control system ensures intimate and uniformly distributed contact between layers, significantly reducing indentation and micro-crack formation in both electrodes and solid electrolyte sheets—enhancing overall cell performance and structural reliability.
- Zero-Damage Material-Handling System
A bionic flexible-suction design combined with precisely modulated airflow buffering enables 100% damage-free, high-efficiency transfer of fragile electrolyte sheets.
A Step-Change in Production Efficiency: Accelerating Industrial Scale-Up
- Integrated Cutting-and-Stacking Platform
The industry’s first fully integrated workflow—ranging from in-line frame fabrication and lamination to electrode cutting and stacking—reduces process-change time to zero. Single-station stacking efficiency surpasses 0.35 s/pcs, delivering unprecedented throughput for gigawatt-scale manufacturing.
- Comprehensive Process Compatibility
A modular architecture supports rapid switching between materials of varying dimensions (length 100–700 mm, width 80–150 mm, thickness 1–30 mm), fully covering validation and mass-production needs across mainstream solid-state battery technologies.
Intelligent and User-Centric Control: A Full-Spectrum Upgrade in Production Management
- Active Micro-Environment Defense
Built-in nano-scale dust capture, hazardous-gas detection and dew-point monitoring systems provide microsecond-level contamination alerts and response, meeting the stringent requirements for ultra-clean and ultra-dry manufacturing environments.
- End-to-End Intelligent Closed-Loop Control
Sensors embedded across the entire production process enable real-time feedback through high-precision visual defect detection. When integrated with predictive-maintenance systems such as PHM, the platform forms the backbone of a highly automated and intelligent production line.
- Human–Machine Co-Optimized Design
With a compact structure and ergonomically designed workstations, the equipment simplifies maintenance and enhances overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), reducing long-term operational costs.
Through the deep integration of cutting and stacking technologies, LEAD has developed a complete process solution covering frame preparation, precision lamination, die-cut forming and high-speed stacking. Its proprietary high-precision, rapid frame-forming process—and its deep understanding of solid–solid interface engineering—delivers a step-change improvement in stacking accuracy and efficiency.
Backed by its self-developed precision-processing system and intelligent production architecture, LEAD’s solid-state battery stacking solution is emerging as a defining technology for the next generation of manufacturing standards. It ensures exceptional product consistency and performance while offering superior pace control and cost competitiveness for mass production—laying robust industrial foundations for the next phase of the global energy revolution.